Europe-Vision for an Organization with 60 Regions
Written by Regionen-Europas.work
Organization
Content
|
On this page we describe organizational features.
|
Cross-National Regulations
Some Cross-National Regulations are issued in the 60 Regions of Europe.
Adjustments to the Law
- National Law should take precedence.
- There is no provision for Regular adaptations of transnational law. The contractual Regulations are rigid.
- The Regulations are general. Demand-oriented adjustments can nevertheless be made.
- Each new National Regulation will be adopted with the knowledge of the Internationally Applicable Provisions.
|
Freedom to Travel
- In principle, the free movement of persons and goods applies.
- The customs and VAT border crossing mechanisms are the same in the 60 Regions of Europe.
- Necessary Regional Regulations are worked out in detail.
- A permit is required for entry from outside. This permit is usually applied for electronically.
Immigration
- Every Nation has Immigration Quotas for three months. The figures are fixed in advance for the whole year.
- The Quotas shall be reviewed by the central office.
- The mechanisms with the establishment quotas are the same in the 60 Regions of Europe.
- Separate Regulations are issued for the domicile of persons from outside.
Border crosser
- Every Nation has border contingents for three months. The rules apply to cross-border commuters from neighbour Nations. The numbers
are set in advance for the whole year.
- The Quotas shall be reviewed by the central office.
- The mechanisms with the border contingents are the same in the 60 Regions of Europe.
Work permits
- Each Nation issues work permits for companies and checks compliance with the law.
- The mechanisms with work permits are the same in the 60 European Regions.
- Separate Regulations are issued for the work permits of persons from outside.
|
Taxes
- Income Taxes should be reduced. A top tax rate of 30% should be the target rate.
- A uniform rate in the order of 0.5 per thousand is levied annually on the assets. The Rules for multiple taxation of assets are worked out in detail.
- The Inheritances within the family are not taxed.
- The Taxes for Companies and Holding companies are to be redefined. The quantity and the payment offices are open topics. Corporate Taxes should be paid to the Regions
that provide the infrastructure. The OECD has now in 2021 adopted a minimum tax rate of 15% on profits of Global Companies.
- Location tax 1: The State-Owned Companies use the infrastructure of the lower political level. State enterprises pay a levy at their sites. The Main Towns are to
make do without financial compensation.
- Location tax 2: Foundations should pay at least one site tax, similar to the one on state enterprises.
- Location tax 3: A location tax should be paid on real estate. As is already common practice in many countries.
Customs and Value Added Tax
- A lot of products imported from outside the 60 European Regions are subject to duty.
- The customs serve to control imports and the competitiveness of local production.
- The duties bring the state revenues.
- The customs system will be simplified. For a large part of the deliveries, customs should be settled by the supplier. This will then be indicated accordingly on delivery.
- VAT will be gradually reduced and probably canceled in some sectors. With the new structures, the state will manage with less revenue from VAT.
|
Energy
- The Electrical Energy Prices should correspond to the costs incurred by the producer. This should apply to private households, small businesses, and large companies.
- In the Energy Sector, the redistribution is to be reduced and yet the energy turnaround is to progress. Taxes on fuel, gas and heating oil are to be reviewed.
|
State organization
The scheme below shows the state organization within the current political order.
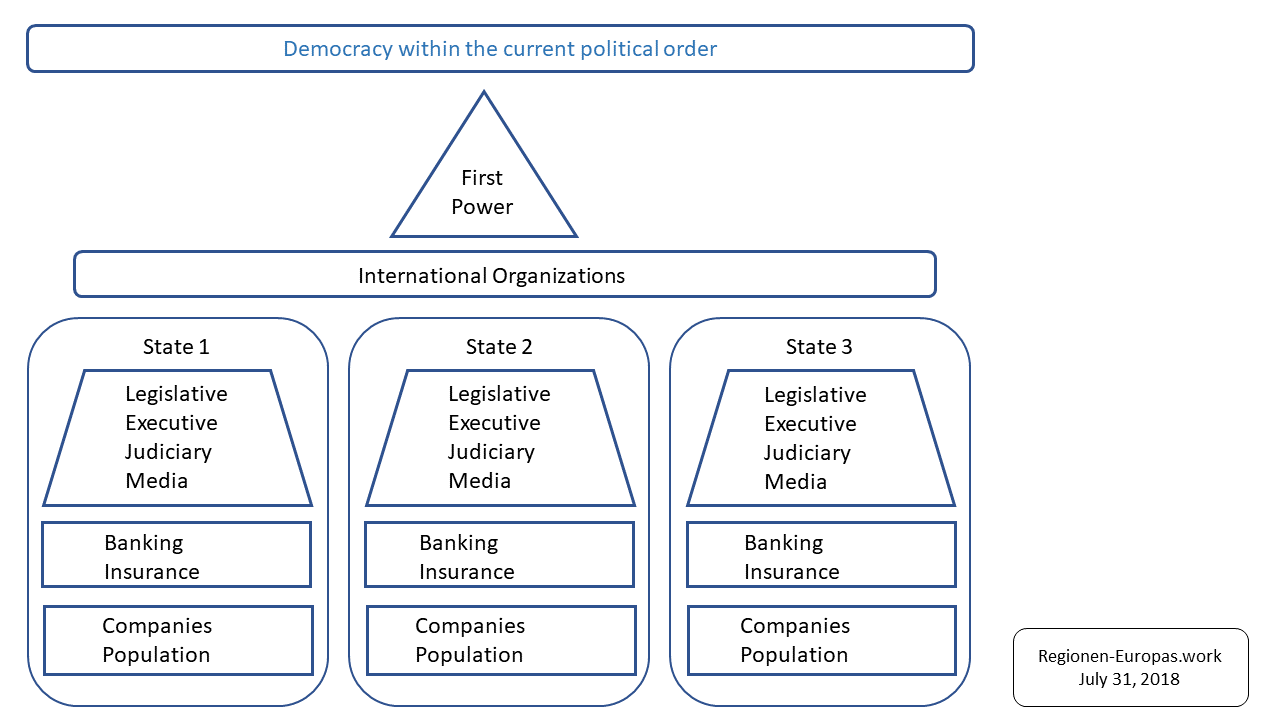
Schematic Representation of the current State Organisation
|
The Blue Banana, an Economic Geographical Model
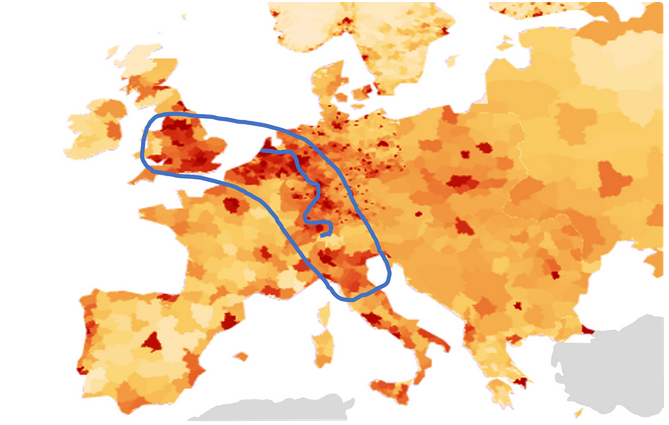
Population density of Europe, River Rhine and Blue Banana, Graphic from Laenderdaten.de edited
|
Text in the ZDF Television Video about the Blue Banana
In the Middle Ages, a city often had only a few 100 inhabitants and the big cities were of course smaller at that time. More than 10,000 people, that was considered a big city. And then there is Cologne, with 40,000 inhabitants, the metropolis of Germany in the 15th century. In general, the places of trade, they are the major attractions. Hamburg, Erfurt, Frankfurt, Nuremberg, these are the major German cities. And only the cosmopolitan cities of Paris, Milan and Bologna break the 100,000 marks. To this day, all these Trading Cities are in the core region of Europe, the so-called Blue Banana. You can see them particularly well at night from space, because the sea of lights of the big cities runs like a band through Europe. Starting in London via Brussels, the cities along the Rhine [River] to Munich and Northern Italy. This is the most densely populated region in Europe and about 40% of the EU population live and work here [in 2015].
|
Our comment on the Blue Banana
The Waterways are of great importance for industry. In our Vision for the 60 Regions of Europe, the Waterways in the various Currency Areas would be increasingly used as
transport routes. The Industry should expanding at various locations.
|
|
|
|
|
The Europe-Vision lives
|
"Make Europe great again", Abbreviation "MEGA"
|
| Europe-Vision Sixty Regions as PDF file
Download PDF
|
Legend:
∗ With one click you get to the corresponding website.
- Intro Graphic: We have edited a graphic from Landkartenindex.de.
- ZDF: Second German Television
|
|
The original text is written in ∗ German. This is a translation.
|
| Last update: April 23, 2024
|
|


